Faculty from the University of Michigan-Dearborn’s Master’s in Robotics Engineering program share what makes this program unique, and explore the exciting opportunities that a Robotics master’s degree can unlock for your future.
Year: 2024
Research Grant for International Collaboration
A new research grant has been awarded. The project title is “Active Inference-based Deep Learning Technology for Automatic Perception and Control of Autonomous Vehicles.” With generous support from Hanyang University, BIMI will investigate an integrated bio-inspired approach for perception and control in autonomous driving through the Active Inference principle until the end of 2026, collaborating with visiting scholars from Hanyang University.
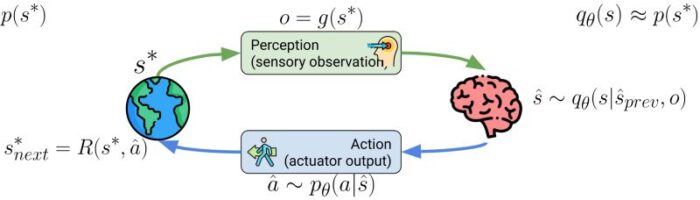
New Collaborative Research with Great Team
A new collaborative research project has been awarded. My lab will develop automatic exploration algorithms for the project.
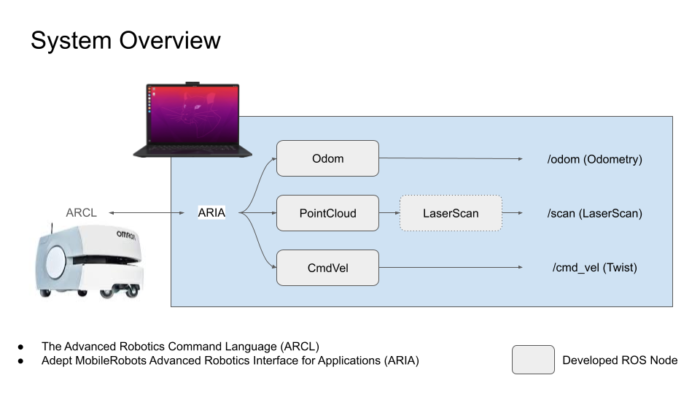
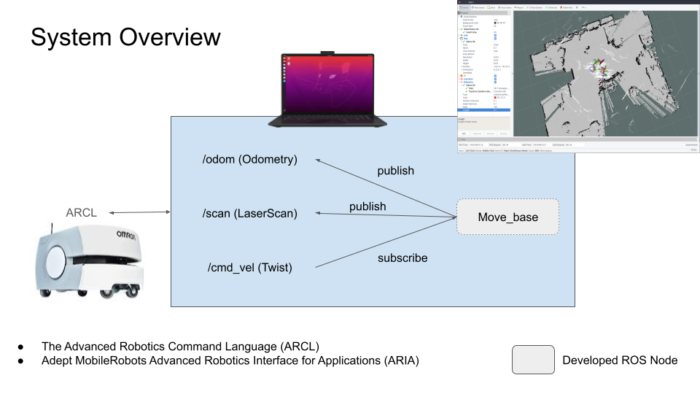
The Office of Research is thrilled to announce an outstanding team of faculty from the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Michigan-Dearborn, led by Samir Rawashdeh, Ph.D. along with Junaid Farooq, Alireza Mohammadi, and Jaerock Kwon has been awarded a one-year, $900,000 grant from MxD for their project titled “Robotic Wireless Signal Strength Mapping of Industrial Facilities.” The Department of Defense (DoD) is the prime sponsor of this project. The project aims to develop an autonomous mobile robot equipped with spectrum analysis and radio hardware to survey wireless signal strength and map it relative to a self-built, two-dimensional layout of the factory floor.
Declined Proposal – NSF CAREER 2023
America needs more farmers. Could robots help?
A new article has been published to share my new project with the UM-Dearborn community through M-REPORTER today.
CECS Assistant Professor Jaerock Kwon is working on autonomous vehicles that could assist farmworkers. But building farm AVs presents a much different challenge than ones designed for the road.
https://umdearborn.edu/news/america-needs-more-farmers-could-robots-help
The Autonomous Plug-In HYbrid Vehicle research platform (APIHYV) finally arrives home
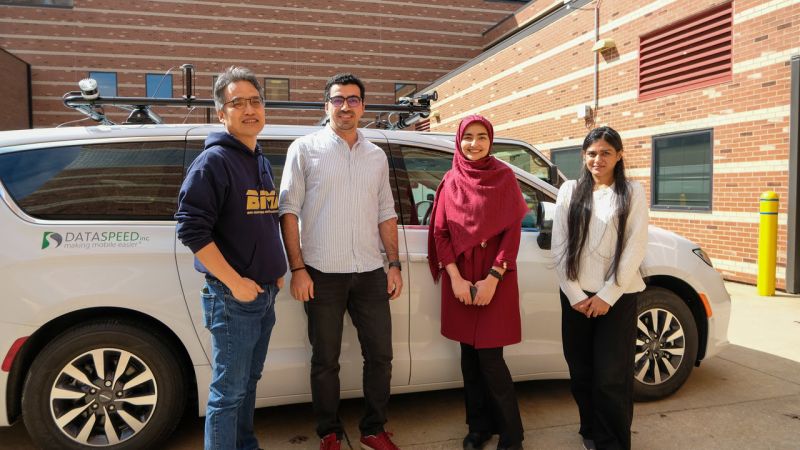

Driverless vehicle research on campus recently got a big boost thanks to a National Science Foundation grant. This new Chrysler minivan from Rochester Hills-based Dataspeed is loaded with a full suite of sensors needed for road-legal, fully autonomous driving, including advanced optical cameras and a LIDAR system for creating 360-degree maps of the surrounding environment. Assistant Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Jaerock Kwon (far left) and his graduate students (from left) Aws Khalil, Elahe Delavari and Feeza Khan Khanzada are among the researchers who will be using the new AV in their research. (Photo by Max Parham) https://lnkd.in/eNGxBR6K
https://www.linkedin.com/posts/department-of-electrical-and-computer-engineering-university-of-michigan-dearborn_driverless-vehicle-research-on-campus-recently-activity-7180936476258414592-ONNU?utm_source=share&utm_medium=member_desktop
PBL in Robotic Manipulation
A New Project: ML for Agricultural Vehicles
Campus Grant awarded
The proposal, “RID: Open-Source Autonomous Ground Vehicular Robotics Platform,” has been awarded for Research Initiation & Development (RID – FY24 Fall Cycle). 1/15/2024 – 1/14/2025.
I am looking for a graduate student who will work on this project during this summer. Please contact me if you are interested in joining this project.
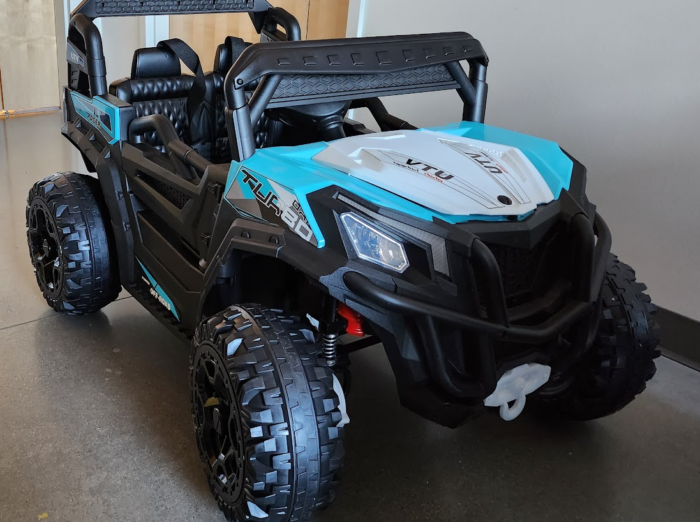

Project Abstract:
The new industry of highly automated mobile robots, including autonomous vehicles, is in high demand for skilled engineers. Engineers for the industry require interdisciplinary knowledge and skillsets, including basic programming skills, electric circuitry, robotic kinematics, machine learning, and Artificial Intelligence (AI). Academia has been trying to respond to the high demand, and there have been efforts to integrate the interdisciplinary knowledge of highly automated intelligent systems, including autonomous vehicles, into their curricula. The integration of the new skillsets or restructuring of the existing curricula is, however, a very challenging task. Some efforts have been made by introducing a small-scale (1/24th, 1/16th, or 1/10th) vehicle to teach the relevant knowledge and skillsets and train researchers and engineers. The MIT RACECAR, F1TENTH, MuSHR, Go-CHART, Dockiebots of Duckietown, and Donkey Car are part of the efforts. A major limitation of the current approaches is in the following two dimensions: (i) The lack of reproducibility owing to heavy craftsmanship requirements due to extensive modifications of the vehicular platform that include removal and replacement of motors, installation of a new ESC (Electronic Speed Controller), custom Printed Circuit Boards, etc. (ii) The restricted onboard processing capabilities due to the platform size (1/24th scale two-wheel or four-wheel differential driving and 1/10th scale Remote Controlled (RC) car). To overcome these major limitations, this project brings forward an innovative idea of building a 1/4th scaled vehicle without extensive modification and providing full-stack software for AI-based perception, planning, and control.