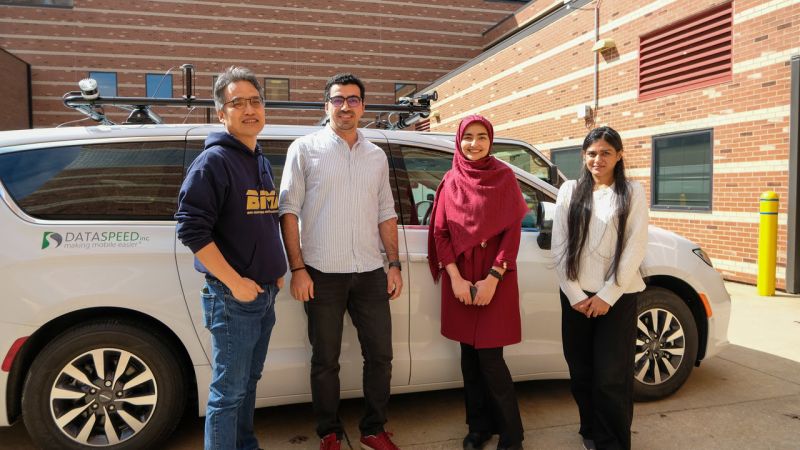
📢 A new NSF grant has been awarded. $200K for two years (10/1/2025 – 9/30/2027).
📑 Title: Predictive Neural Dynamics for Latency Mitigation in Autonomous Driving.
🏛️ Abstract:
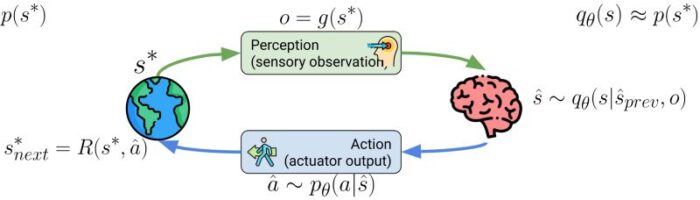
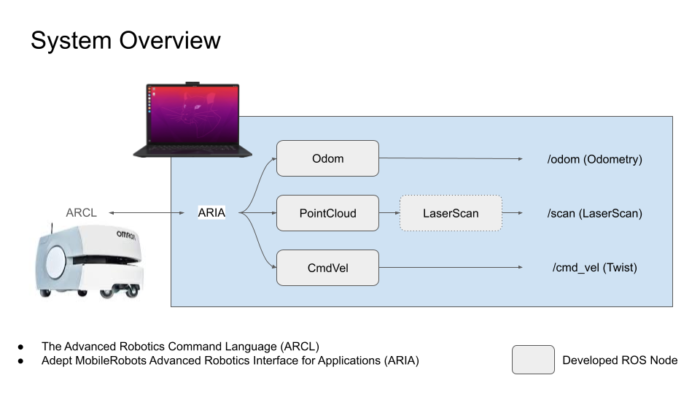
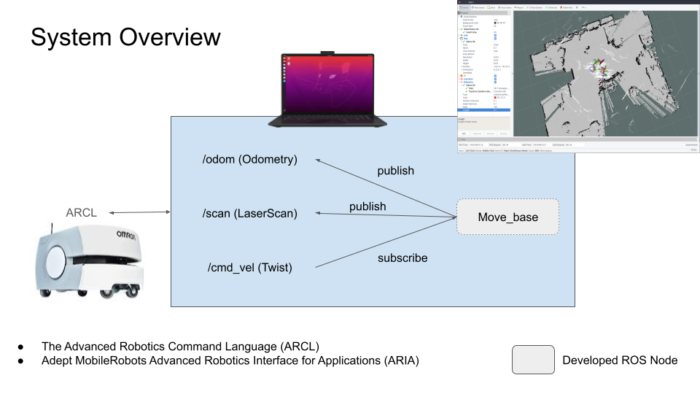
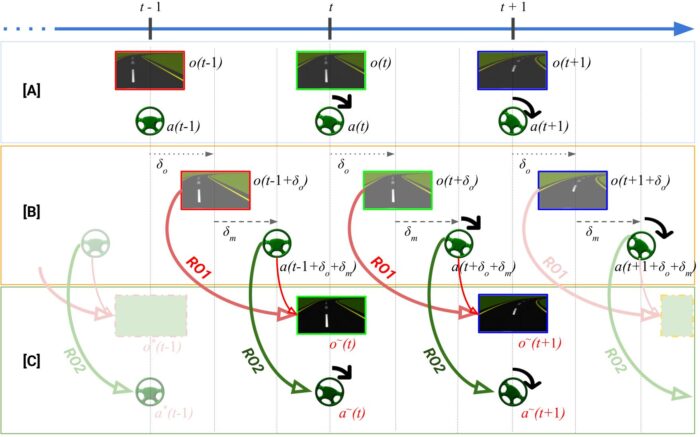
Autonomous vehicles are regarded as a transformative technology with the potential to enhance safety, efficiency, and accessibility in transportation systems. However, a critical challenge, preventing their widespread adoption, is the delay between when sensors detect environmental changes and when the vehicle responds with appropriate actions. This latency, frequently quantified in milliseconds, can determine the difference between navigating safely around a suddenly appearing obstacle and experiencing a collision. The prevailing solutions utilize costly, high-performance hardware to mitigate these delays, rendering autonomous vehicles expensive and inaccessible to the general public. This project aims to address this fundamental challenge by developing intelligent systems that can predict what sensors will detect in the immediate future and prepare appropriate responses in advance, thereby effectively eliminating the negative effects of processing delays. The research has the potential to enhance the safety, reliability, and cost-effectiveness of autonomous vehicles, thereby facilitating their integration into society’s transportation infrastructure. Beyond the realm of autonomous driving, this technology has the potential to enhance various applications, including remotely operated vehicles, delivery robots, and search-and-rescue systems. These domains necessitate rapid and precise responses to environmental changes, which are critical for ensuring safety and optimal performance.
More details:
🔗 https://lnkd.in/e5D63s2A